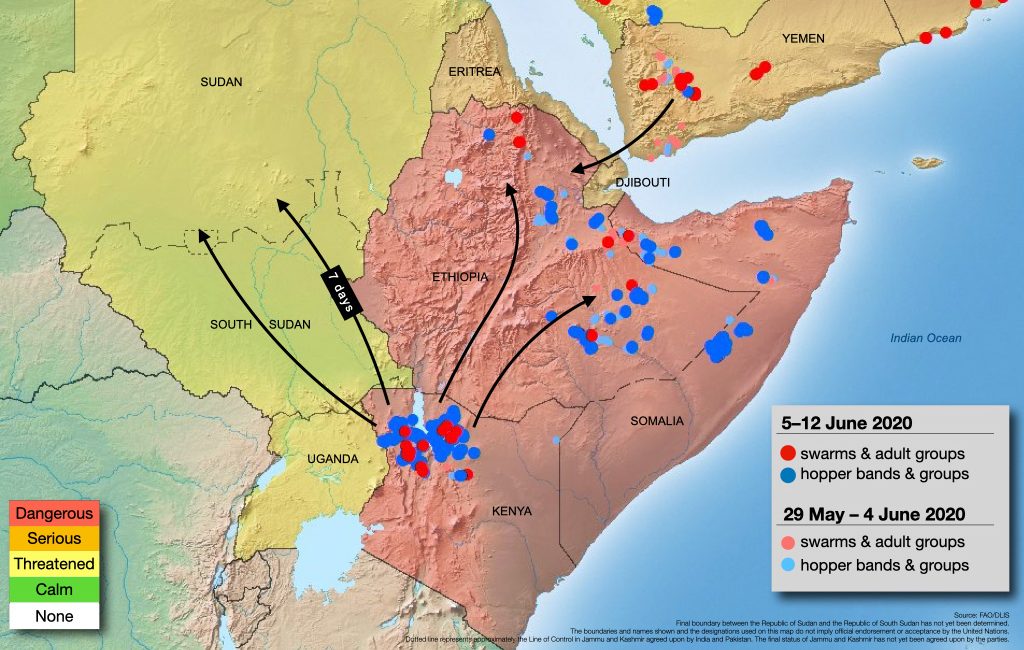
A second-generation of immature swarms have now started to form in northwest Kenya according to the latest FAO Locust Watch report. Swarm formation will continue for about four weeks while the bulk of the swarms will form during the second half of June.
The report says prior to migration, swarms will remain for a short time during which there is a considerable threat to crops and pastures in Turkana and Marsabit counties. From about 15 June, an increasing number of swarms are expected to migrate northwards with the prevailing winds to Ethiopia and Sudan. In Ethiopia, swarms are likely to first appear in the south and continue to Oromia, Somali, Amhara, Afar and Tigray regions.
It will take about one week for swarms to migrate from northwest Kenya to Sudan. During that time, they will traverse South Sudan (mainly east of Juba, Bor, and Malakal) and perhaps northeast Uganda, before reaching the extreme southern summer breeding areas of Sudan (South Kordofan, West Kordofan, East Darfur, South Darfur, White Nile, Blue Nile). From there, some swarms may continue to North Kordofan, North Darfur, and perhaps West Darfur. Other swarms may appear in states adjacent to Ethiopia (Sennar, Al Qadarif, Kassala).
If swarms reach Sudan and find dry conditions, then they are likely to migrate to eastern Chad and continue westwards across the Sahel of West Africa. This threat should decline progressively during the next four weeks as the summer rains commence in Sudan.
Locusts – latest report
- Tags: Ethiopia, Food security, Kenya, Locusts, South Sudan, Sudan, Uganda
Share your views about this story
Related stories

Ethiopia Shifts from Emergency Relief to Climate Resilience through Water Investment says Ministry
Ethiopia has transitioned from short-term emergency responses to a long-term climate resilience strategy centred on

Ethiopia Launches OpenAgriNet Digital Network Initiative to Modernize Agricultural Data Systems
The Ethiopian Agricultural Transformation Institute (ATI) has launched Ethiopia OpenAgriNet (Ethiopia OAN), a national digital

Ethiopia Scales Up Agricultural Mechanization with Chinese Technology
The Ethiopian Ministry of Agriculture and the Agricultural Research Institute have partnered with Chinese agricultural

Bioeconomy Takes Centre Stage as Kenya and Sweden Advance Joint Industrial Agenda
By Kimuri Mwangi Kenya and Sweden have renewed their commitment to strengthening collaboration in the
How the COMESA Competition Commission Rescued Eswatini from Looming Hunger and Maize Seed Lockout
By Kimuri Mwangi The COMESA Competition Commission (CCC) successfully intervened to resolve a maize seed

COMESA Competition Commission Calls for Regional Unity to Ease Food Trade Barriers Across COMESA
By Kimuri Mwangi The COMESA Competition Commission recently held its third press conference in Nairobi,

COMESA Competition Commission Recognised for Tackling Food Inefficiencies
By Kimuri Mwangi The COMESA Competition Commission (CCC) has earned global recognition for its efforts

FAO Urges Vigilance as Desert Locust Threat Intensifies in Northwest Africa
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) is calling on countries in

Ethiopia Highlights Agricultural Reforms at BRICS Ministerial Meeting in Brazil
Ethiopia participated in the BRICS Ministerial Meeting on Agriculture held in Brasília, with the country

Ethiopia’s Agriculture Sector Drives Economic Growth, says Minister
Ethiopia’s agriculture sector continues to play a critical role in the country’s economic development, Minister

